Author: Chase Snyder, Sr. PMM, Xage Security
Privileged Session Management (PSM) plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access and potential breaches. But PSM isn’t a standalone product. It tends to be offered as a feature of Privileged Access Management (PAM), and the session management capabilities are not consistent between providers. There is even a whole product category called Privileged Account and Session Management (PASM), devoted to delivering the right set of capabilities in a single package.
The importance of comprehensive PSM has been underscored by many cyberattacks and insider threats over the years. Since Valid Accounts (MITRE T1078) are so commonly abused in cyberattacks, it is vital not only to prevent unauthorized access, but to control, in real time, what a privileged account is able to do when accessing sensitive assets. This blog post delves into five critical capabilities essential for effective PSM, each serving as a fundamental pillar in equipping security teams to combat modern cyber threats.
PAM, PASM, PEDM…What’s The Difference
Gartner identifies four categories of Privileged Access Management tools, and only one explicitly includes session management as a capability. But the fact is that any enterprise that needs to manage privileged access at all would benefit from being able to manage and record sessions. Those with access management tools that lack privileged session management will probably end up either purchasing another tool to enable session management, at least for some subset of users in their organization. This is a step down the path of tool fragmentation that leads to management and budget challenges. Better to get a single tool with all the features you need.
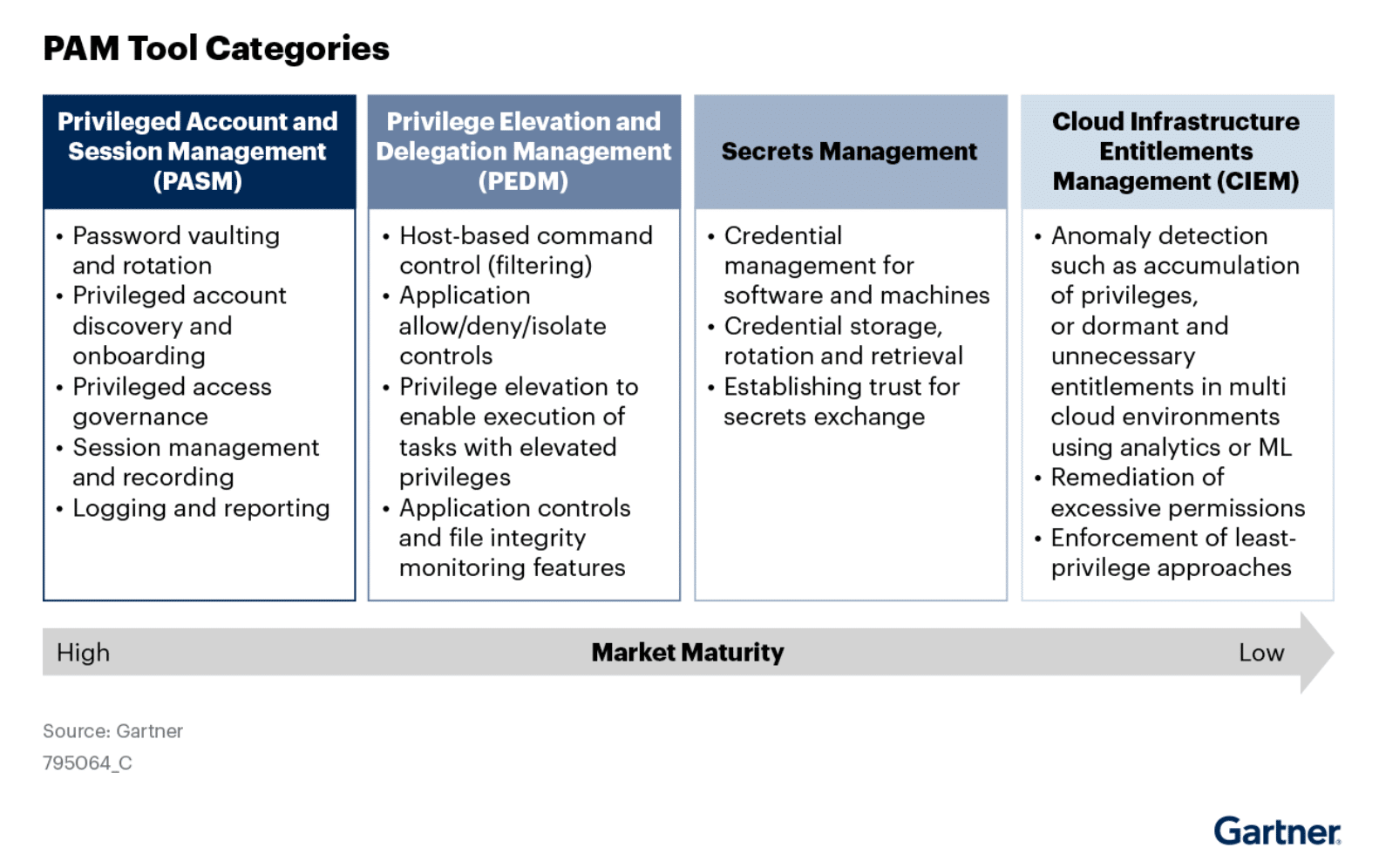
In general, tool category only offers a loose approximation of the capabilities any specific tool might offer. It is important to dig in deep and understand both your own enterprise’s specific needs, and the capabilities on offer from any vendor you consider. When seeking Privileged Access Management, Privileged Session Management, or any combination thereof, here are several capabilities that must be considered, especially along the lines of just-in-time methods.
1. Securely Enabling Users, Including Third Party, to Access Critical Systems
The ability to securely enable user access to critical systems is a balancing act between accessibility and security. This balance is achieved through robust authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and the use of secure, encrypted channels for access. Many businesses now rely on third party contractors, extended workforces, and even OEMs for some level of support. These users need privileged access, and can create third party risk inside the enterprise environment. This is a type of privileged session that urgently needs management, that many PSMs are not currently able to deliver in a timely manner. One key source of just-in-time advantage for a PAM or PASM provider is the speed at which a third-party privileged account can be provisioned, then revoked once the work is done.
For authenticating these sessions, MFA alone is not sufficient. Attackers have grown proficient at subverting SMS-based MFA by social engineering or outright bribing mobile carrier employees into swapping SIMs for them in order to gain access to target environments (like the MGM group in 2023, for instance). Enforcing MFA at multiple layers or hops within the session provides another layer of protection for critical systems.
Techniques like enforcing least privilege access also play a key role, ensuring users have only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks, minimizing the risk of privilege abuse. Secure access not only protects the system from external threats but also mitigates the risk of insider threats, making it a cornerstone in the structure of privileged session management.
2. Monitoring for Suspicious or Unauthorized Activities
Continuous monitoring and recording of privileged sessions is akin to having a vigilant guardian overseeing the activities within your network. This involves deploying advanced tools that can detect unusual patterns that may allow them to prevent a data breach. Suspicious activities such as unauthorized access attempts, logins from unusual locations, the same account being logged in from multiple locations, or other strange user behaviors can all provide a signal that suspicious or unauthorized activities are underway.
By proactively monitoring these sessions, organizations can quickly identify and respond to potential security incidents. This real-time surveillance is crucial for maintaining the integrity of PSM, as it allows for the early detection of potential breaches or misuse, thereby enabling timely intervention to prevent full-scale attacks.
3. Session Recording and Audit Trail
Maintaining a detailed record of all activities within privileged sessions, including who accessed what and when, is imperative for a robust PSM strategy. Session recording and audit trails serve multiple purposes. Firstly, they provide invaluable insights for post-event analysis, helping to understand how a security incident occurred and how to prevent similar occurrences in the future. Secondly, these records are crucial for compliance purposes, as many regulatory frameworks require detailed logs of access and activities within critical systems. The presence of an exhaustive audit trail not only strengthens security but also fosters a culture of accountability and transparency within the organization.
4. Real Time Session Termination to Protect Critical Systems
The ability to terminate privileged sessions in real-time is an essential emergency response mechanism in PSM. This is one of the key “just-in-time” differentiations available, but not universally present, in PAM offerings with PSM capabilities. In the event of detecting suspicious activities or a confirmed breach, having the capability to immediately cut off access can be the difference between a minor security incident and a catastrophic breach. This rapid response mechanism is especially vital in scenarios where session tokens are compromised, as it can prevent attackers from further exploiting the access. Implementing real-time session termination capabilities demonstrates an organization’s commitment to proactive security measures, ensuring the protection of critical systems even in the face of imminent threats.
5. Distributed Credential Vaulting and Automated Password Management
Storing usernames and passwords securely is a foundational requirement for preventing the theft and misuse of those credentials. Distributed password vaulting is more secure than a centralized one, and can prevent attackers from stealing your enterprise credentials and using them against you, or selling them for profit on the dark web.
Privileged Session Management is a crucial line of defense against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. There are layers and maturity levels in privileged access management, from managing and storing credentials to managing what those credentials can do, then managing what they are actively doing. If any layer is missing, a there’s a crack for an attacker to wedge themselves into.
The integration of PAM with zero trust policies, secure user access, continuous monitoring, session recording, and real-time session termination forms a comprehensive approach to safeguarding privileged sessions. By adopting these critical capabilities, enterprises can not only enhance their security posture but also build resilience against the relentless wave of cyberattacks. The journey of cybersecurity is one of constant evolution, and staying ahead means continuously adapting and strengthening our defenses, with effective Privileged Session Management being a cornerstone of successful defense.
Learn more about Xage’s Zero Trust Privileged Access Management and session management capabilities.










