Susanto Irwan, Co-Founder, President, and CTO, Xage Security
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping the enterprise, but it’s also breaking traditional security models. As organizations adopt large language models (LLMs), agentic AI, Model Context Protocol (MCP) and A2A, they’re discovering that existing defenses can’t keep up.
AI implementations aren’t static apps—they’re dynamic, interconnected ecosystems. They span cloud, on-premises, and edge environments, linking autonomous agents, APIs, and sensitive datasets. A single prompt or automation chain can trigger actions, leak confidential data, or even manipulate downstream systems.
The result? A new and growing attack surface—where data leakage, rogue agents, and insider threats are all real possibilities.
The AI Security Gap: From LLMs to Agentic AI
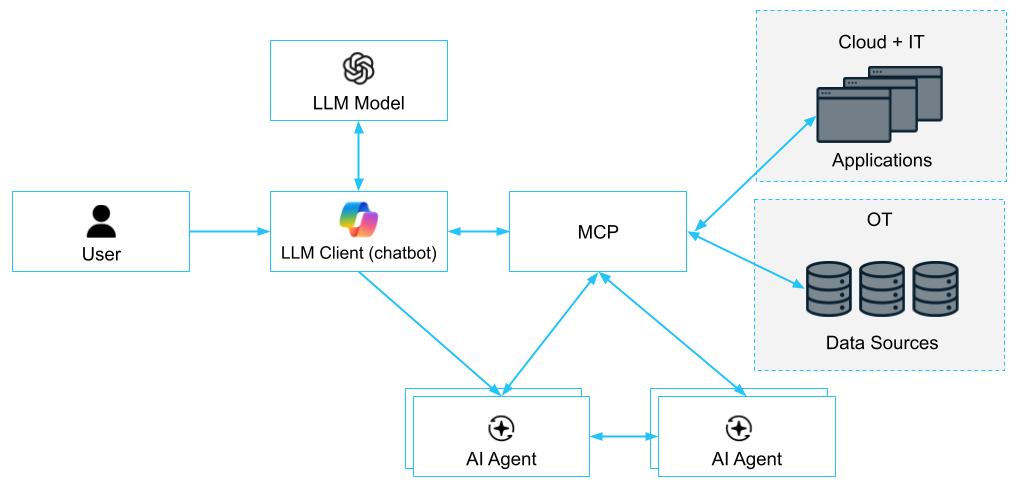
In today’s AI-driven workflows, interactions are diverse, complex, and happen across network zones. These are many-to-many interaction (e.g. AI-agents ↔ AI-agents) that take place across sensitive systems (e.g. user→LLM→private data, RAG→private data). Some examples of the sorts of interactions that take place:
- A human user prompting a chatbot
- That chatbot engages an AI agent
- The agent, or an associated LLM, retrieves sensitive data via MCP
- The agent interacts with internal and external APIs
- Multi agent to agent interactions
Each hop carries its own security risks. Without fine-grained, identity-aware control, privileges can easily leak from one entity to another, exposing sensitive information or enabling unauthorized actions.
Agentic AI—AI that can take initiative, chain actions, and orchestrate tasks—only magnifies this risk. While agentic capabilities unlock efficiency and automation, they also create potential for unintended, unapproved, or malicious behavior if not properly governed.
Why Prompt Filtering Isn’t Enough
Most AI security strategies rely heavily on prompt and output filtering, LLM firewalls, or guardrails, all of which rely on their own interpretation of the natural language inputs and outputs going to and from AI components . While these measures can have their place, they’re not bulletproof.
Natural language is ambiguous, flexible, and context-dependent, making natural-language-level defenses inherently vulnerable to jailbreak attacks. As a result, sophisticated or automated attacks can bypass filters, guardrails and LLM firewalls with creative prompts or by exploiting indirect prompt injection. While natural-language-level keyword-based and heuristic filtering can catch simple phrases, more sophisticated and creative attackers can manipulate and bypass these protections. And even without malice, well-meaning users or agents may inadvertently access or share restricted data.
To truly secure AI, controls must live beneath the prompt level—at the network/application/API protocol and identity communication layer, which does not involve natural language interpretation—so that controls can’t be bypassed by social engineering of LLMs or AI agents.
Xage Zero Trust for AI: A Better Way Forward
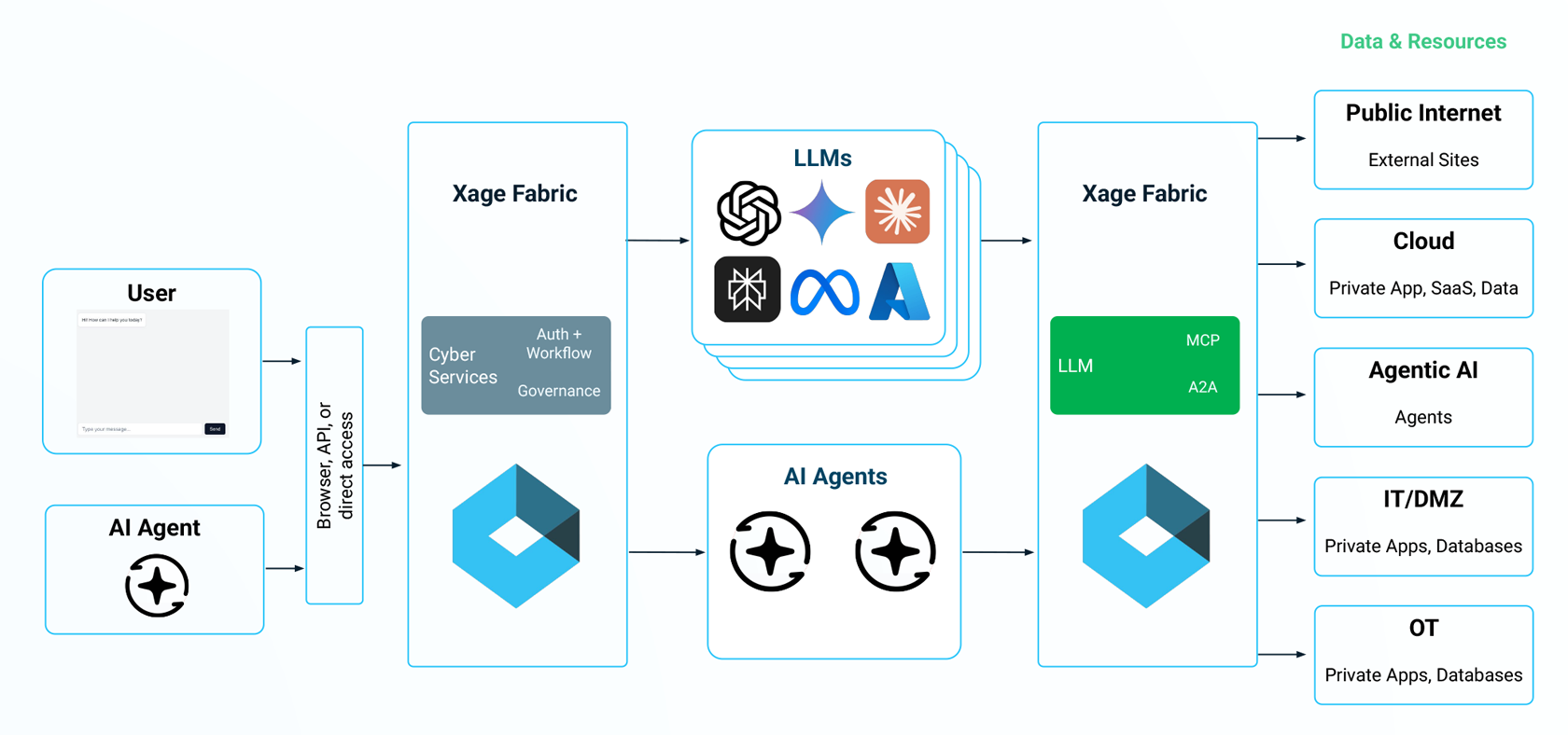
Zero Trust flips the traditional trust model. Instead of granting broad access, every interaction—whether human-to-agent, agent-to-agent, or agent-to-data—is permitted only if authenticated and authorized.
Xage brings Zero Trust to AI security. With Xage, AI security is:
- Identity-based: Every user, AI agent, data sources, and LLM has a unique identity and precise access policies. Entitlements are required for every interaction.
- Just-in-time & just-enough privilege: Access is granted only when needed, for the minimal scope necessary, with least privilege.
- Continuous and Multi-Hop: Policies are enforced from initial request to final output, and identities are traced across every hop of every workflow’s chain of interactions.
- Comprehensive: Access to data across Cloud/IT/OT with proper zero trust enforcement.
- Preventative and Jailbreak-Proof: Data leakage, rogue AI behaviour, and chatbot misuse are definitively blocked.
- Resilient: Even if one component is compromised, the attack is contained, and the attackers cannot escalate privileges or pivot to other systems.
Highlighted Use Case: AI Chatbot Policy Enforcement and Governance
When AI chatbots are connected to sensitive systems—such as HR databases—fine-grained, identity-based access control is essential. Xage enables safe AI usage by enforcing authentication, authorization, and tamper-proof auditing at every step, ensuring that users and AI agents only perform the actions they’re authorized to take. Whether using third-party tools like Microsoft Copilot or custom in-house chatbots, Xage ensures organizations can securely leverage AI while preventing both internal and external data leaks.
In this highlighted use case, a Microsoft Copilot chatbot is connected to an HR database. The Xage Fabric enforces strict controls: an unauthenticated HR user is blocked from viewing salary data until they log in. Then, the authenticated user can view—but not update—employee salaries unless explicitly granted write access, and all interactions are fully logged. This demonstrates how Xage enables organizations to safely unlock AI while maintaining complete visibility and control over sensitive data.
Enterprise AI Chatbot Example (Protected by Xage Fabric)
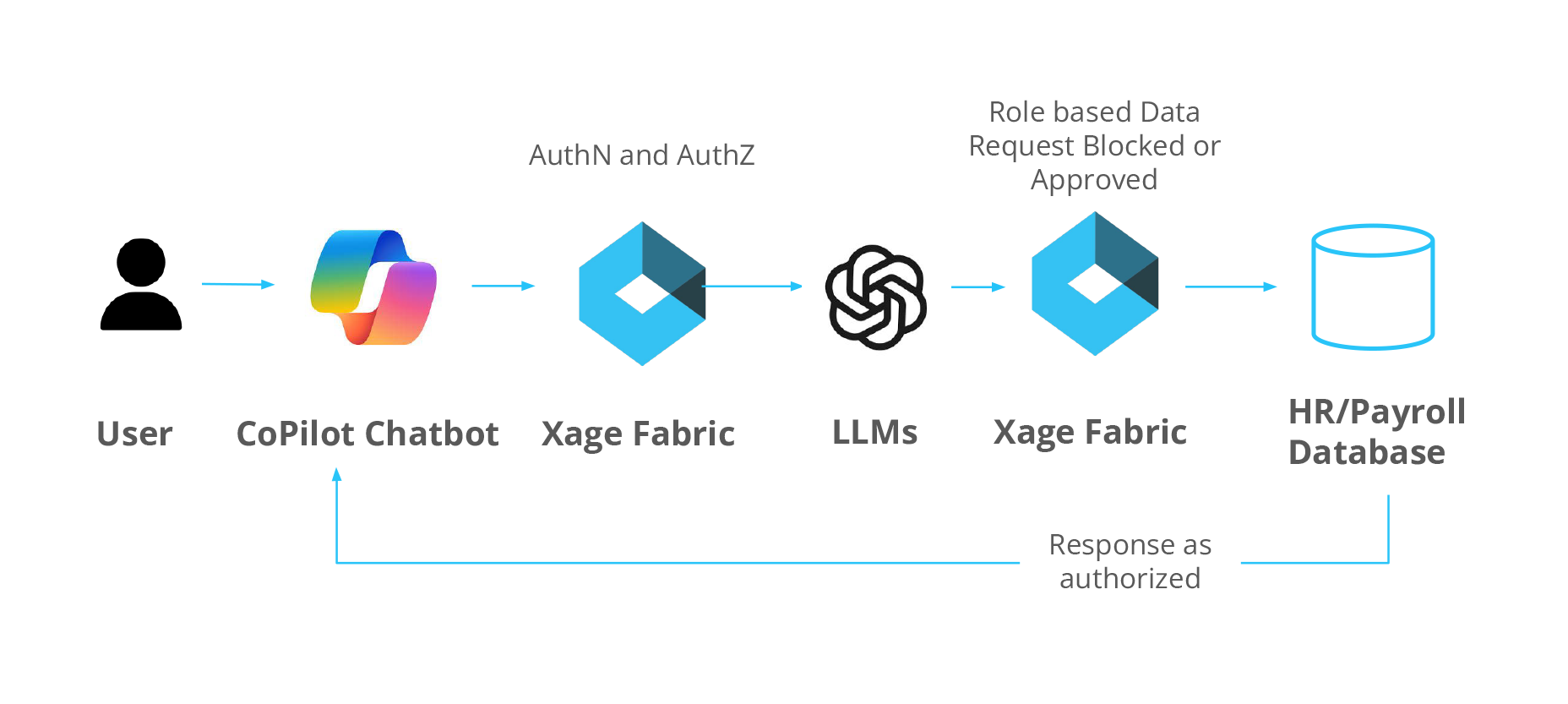
With Xage, organizations can benefit from the potential of AI—while ensuring that each data request is validated against the user’s access rights, preventing oversharing, misuse, or data leakage.
Securing MCP Pipelines and Multi-Agent A2A Workflows
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) and Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol are rapidly becoming the backbone of AI orchestration—allowing agents, LLMs, and tools to communicate in a standardized way. But MCP and A2A need to be protected by strong, standardized, and secure authentication and authorization controls.
With Xage applied to MCP and A2A, every request—whether from a human or another AI system—must be authenticated, authorized, and aligned to policy. This closes gaps that attackers could exploit to exploit your AI deployment.
For multi-agent and multi-hop workflows, Xage ensures that access entitlements are preserved end-to-end. If an agent can act on data, it’s only because both the agent and the initiating user have the correct privileges.
Governance and Compliance
Xage’s Zero Trust for AI isn’t just about stopping attacks—it’s also about maintaining trust, auditability, and compliance.
Xage can help organizations:
- Enforce compliance with frameworks like NIST 800-53, ISO 27001, SOC2, and GDPR.
- Log every interaction in a tamperproof, quantum-proof store for auditing and investigations.
- Apply AI protections such as tokenization and sanitization before sensitive data or requests reach an LLM, AI agent, and users.
The Payoff: Secure AI Innovation
With Xage, enterprises can safely deploy AI without losing control over data, systems, workflows, or automated behaviours. This means:
- LLMs and agentic AI can be used across departments without introducing data leakage risk.
- MCP and A2A pipelines can orchestrate powerful automation without becoming backdoors for attackers.
- AI adoption accelerates because security policies integrate seamlessly with existing identity and access controls—no re-tagging, no infrastructure rework.
- AI Return On Investment: By enabling AI to be used securely with your organization’s most important systems and data, AI’s positive impacts are maximized.
The result? Innovation without compromise—and the ability to leverage AI at scale, securely and responsibly.
Learn how to protect your AI initiatives. Get the Solution Brief for a deep dive, or join our co-founders for an upcoming webinar to discover how Zero Trust for AI can help secure your organization.










